
When this fossil is completely excavated, it will shed light on several questions about this species (if it is designated as an Au. He dubbed this fossil "Little Foot", and has since found that it comes from a 3.3-million-year-old partial skeleton, most of which is still embedded in the cave sediments. In 1994, scientist Ron Clarke found four left early human foot bones while searching through boxes of fossils at Sterkfontein, a site in South Africa where most Au.africanus part of the lineage that led to our own species, Homo sapiens? Where did it come from? Was it a descendent of Au. Made in USA Gorillas are ground-dwelling, predominantly herbivorous apes that inhabit the forest of central Sub-Saharan Africa.
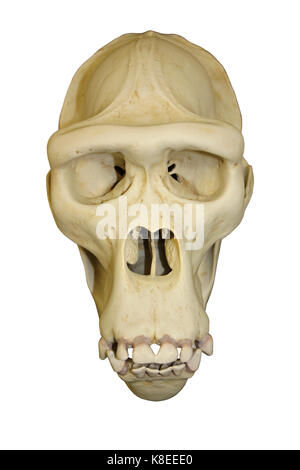

Size: 10 inch (26cm) Museum quality Cast in durable Polyurethane resins. Tropical and mountain rain forests of Equatorial Africa. africanus is currently the oldest known early human from southern Africa. Shipping Info Related Easy Returns Gorilla Skull, Male. africanus that may be answered with future discoveries: We don’t know everything about our early ancestors-but we keep learning more! Paleoanthropologists are constantly in the field, excavating new areas, using groundbreaking technology, and continually filling in some of the gaps about our understanding of human evolution.īelow are some of the still unanswered questions about Au. africanus ate tough foods but also had a very variable diet including softer fruits and plants. africanus teeth compared to a contemporaneous species, P. Dental microwear studies found more scratches than pits on Au. africanus may have eaten from looking at the remains of their teeth-tooth-size, shape, and tooth-wear can all provide diet clues. africanus individuals had a diet similar to modern chimpanzees, which consisted of fruit, plants, nuts, seeds, roots, insects, and eggs. africanus individuals, too.ĭespite the carnivorous preferences of their contemporaneous predators, Au. africanus as weapons however, in the 1970s and 1980s, other scientists began to recognize that predators such as lions, leopards, and hyenas were instead responsible for leaving these broken animal bones. Dart assumed these broken animal bones, teeth and horns were used by Au. Raymond Dart created the term ‘osteodontokeratic’ culture (osteo = bone, donto = tooth, keratic = horn) in the 1940s and 1950s because remains of this species were found alongside broken animal bones. africanus fossils however, for a long time researchers believed Au. No stone tools have been discovered in the same sediments as Au.
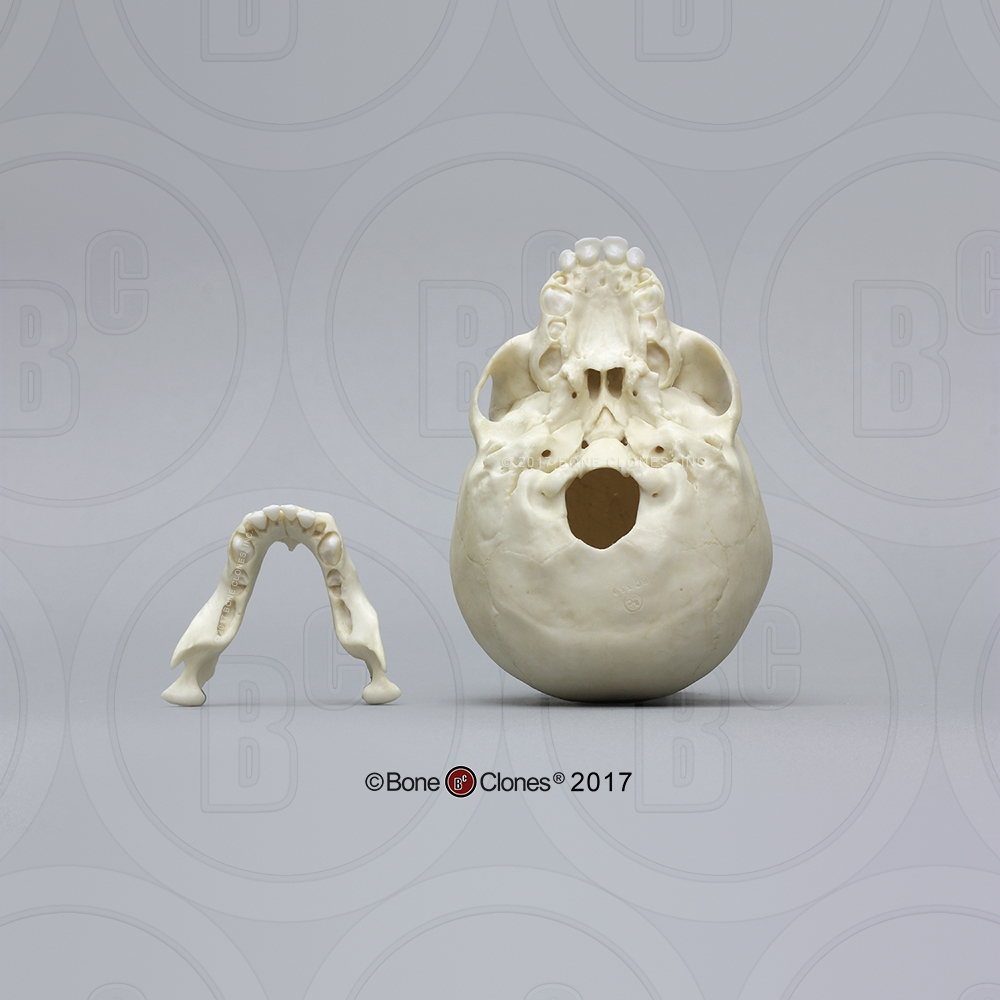
GORILLA SKULL VRS AFRICAN SKULL ARCHIVE
Digital Archive of Ungulate and Carnivore Dentition.Adventures in the Rift Valley: Interactive.Smithsonian National Museum of Natural History The Smithsonian Institution's Human Origins Program Main Menu


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
