
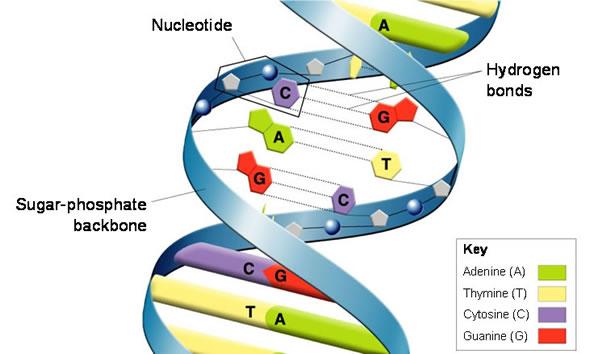
Dispersive replication would have produced all intermediate chromosomes with a range of densities. Conservative replication would preserve the original chromosome. The experiments of Meselson and Stahl showed that second generation DNA was a combination of original strands with new strands and third generation DNA also contained some completely new chromosomes. Which of the following is the name of the process through which DNA replicates?ī is the correct answer. B is incorrect because due to size restrictions, purines always pair with pyrimidines. Choices A and D are incorrect because bases do not pair with themselves. In double-stranded DNA, how do the four bases (C, A, T, G) pair up with each other?Ĭ is the correct answer. The results showed DNA of only two different densities, exactly as predicted by the semi-conservative model. However, an even less dense DNA would also be present that had two strands containing only newly synthesized all 14N strands. One would contain DNA with an all 15N DNA strand and an all 14N DNA strand. According to the dispersive model, the resulting DNA would still have a range of intermediate densities.Īccording to the semi-conservative model, two different densities of DNA would be present. In order to decide which of the remaining two models was correct, the remaining bacteria were allowed to replicate a second time. However, the dispersive model would also produce DNA with an intermediate density. This is exactly what was found and this result eliminated the conservative model from consideration. This difference in density would show up when the extracted DNA was centrifuged. It was hypothesized that any new DNA synthesized during this single replication would be less dense than the original DNA because it would have an all 15N DNA strand and an all 14N DNA strand. These bacteria were then transferred to a medium containing only the lighter isotope, 14N, and cultured for one more generation. coli bacteria were cultured in a medium that contained a heavy isotope of nitrogen, 15N. Matthew Meselson and Franklin Stahl devised an experiment using different isotopes of nitrogen in bacterial cultures. In the dispersive model, each strand of both copies contains a mixture of old and new DNA fragments.īefore biologists could tackle the problem of the details of DNA replication, the correct model had to be identified. In the conservative model, the parent DNA remains intact and an all new copy is created. Two other models of DNA replication were considered. The Watson and Crick model for DNA replication is also known as a semi-conservative model. Each DNA molecule consists of one “parent” strand and one “new” strand. The result is two DNA molecules identical to the original.The new nucleotides join together to form the sugar-phosphate backbone of a new strand of DNA.Each original DNA strand attracts new nucleotides that plug into their complementary bases on the original strand.The original double helix separates into two separate strands of DNA.So DNA replication would occur in a few simple steps: Watson and Crick reasoned that, since the hydrogen bonds were weak, the double helix of DNA somehow “unzipped” into two strands. Even hot water is enough to cause the base pairs to separate. The hydrogen bonds holding the base pairs in a DNA molecule together are relatively weak compared to other chemical bonds. Due to chemical and physical restraints, base pairs can only form from adenine and thymine (A-T) or guanine and cytosine (G-C). Each “rung” on the DNA molecule consists of a pair of nucleotide bases.Each polymer molecule consists of a sequence of nucleotides. Based on x-ray data, Crick, Watson, and many others determined the structure of DNA to be a twisted, double helix of two polymers.Over many decades, biologists had concluded that genetic information was passed from generation to generation by the material known as deoxyribonucleic acid, or DNA.In this lesson, you will review the process by which DNA and RNA are replicated in a cell.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
